وظایف routine به صورت خودکار با استفاده از Extention ،Attribute و Reflection درNET.
شنبه 19 دی 1394Reflection به معنی توانایی یک برنامه در اینکه خود را مشاهده کند و رفتار خود را اصلاح کند .با استفاده از Reflection می توان در زمان اجرا جزییات مربوط به برنامه را بررسی کرد و در صورت نیاز اقدام به تغییر آن کرد.
Reflection به معنی توانایی یک برنامه در اینکه خود را مشاهده کند و رفتار خود را اصلاح کند .با استفاده از Reflection می توان در زمان اجرا جزییات مربوط به برنامه را بررسی کرد و در صورت نیاز اقدام به تغییر آن کرد.
فضای نام System.Reflection در محیط دات نت به ما امکان reflection را می دهد .به عبارت دیگر امکان وارد شدن در متادیتاهای اسمبلی و بررسی آن ها را برای ما فراهم می کند. در این فضای نام کلاس هایی وجود دارند که در زمان اجرا به ما امکان دیدن اطلاعات اسمبلی در حال اجرا و یا هر اسمبلی دیگری را می دهند . . این اطلاعات شامل: توصیف کاملی از کلاسها، Structure ها(مفهوم structure در سی شارپ را در لینک آن مطالعه کنید )، کلاسهای پایه، Interface ها، Enumeration ها و حتی متدها و Property ها و … مربوط به هر اسمبلی است.
در این مقاله قصد داریم نحوه اتوماتیک سازی یک سری از کارهای تکراری با استفاده از Extentions و Attributes و Reflection را آموزش دهیم
اعتبارسنجی و و فرمت کردن اشیا از کارهای روتین هر برنامه ای است .برنامه نویسان از برخی فرم ورک ها و ابزارها برای مدیریت این کارها استفاده می کنند .اما به صورت ساده در اینجا از امکان Attributes و Extentions برای این کار استفاده می کنیم .
سناریویی که در پیش گرفته ایم به این صورت است که
سن باید بین 1 تا 100 باشد و خارج از این محدوده برای ما دارای اعتبار نیست.
اسامی که در برنامه ما وجود دارد باید به صورت اولین کلمه بزرگ ، باشد .یعنی تمامی حروف کوچکند به غیر از حرف اول
و مورد سوم این است که اسامی در خارج از کلاس قابل نمایش نباشند.و باید به صورتی نمایش داده شوند که نام به نام خانوادگی چسبیده شود و به صورت نام کامل نمایش داده شود .
در ادامه کلاسی به نام Person تعریف می کنیم .
Person.cs
public class Person
{
public int Age { get; set; }
public string FamilyName { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string FullName { get; private set; }
}
یک کاری که مطمئنا در اکثر پروژه های خود انجام می دهید این است که برای پراپرتی ها کلاس صفت های مناسب تعریف کنید
Person.cs
public class Person
{
[RangeValidator(1, 100)]
[IsOddNumber]
public int Age { get; set; }
[ToUpper(ToUpperTypes.FirstAndAfterSpace)]
public string FamilyName { get; set; }
[ToUpper(ToUpperTypes.FirstLetter)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[AutoPupulate("Name", "FamilyName")]
public string FullName { get; private set; }
}
دوباره به کد بالا نگاه کنید هر چند ساده به نظر می رسند ولی در واقع این صفت هایی که داده ایم هیچ کاری انجام نخواهند داد .چرا ؟ برای اینکه این صفت ها جزو صفت های MVC نبودند و ما آن ها را ساخته ایم ، پس مجبوریم که پیاده سازی خاص آنها را هم بنویسیم
RangeValidatorAttribute.cs
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property,AllowMultiple =true)]
public class RangeValidatorAttribute : Attribute
{
public int MaxValue { get; set; } // Maximum acceptable value
public int MinValue { get; set; } // Minimum acceptable value
public RangeValidatorAttribute(int MinValue, int MaxValue)
{
this.MaxValue = MaxValue;
this.MinValue = MinValue;
}
}
IsOddNumberAttribute.cs
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property,AllowMultiple =true)]
public class IsOddNumberAttribute : Attribute
{
}
ToUpperAttribute.cs
public enum ToUpperTypes
{
FirstLetter,
FirstAndAfterSpace,
AllLetters
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true)]
public class ToUpperAttribute : Attribute
{
public ToUpperTypes Type { get; set; }
public ToUpperAttribute(ToUpperTypes Type = ToUpperTypes.AllLetters)
{
this.Type = Type;
}
}
AutoPupulateAttribute.cs
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class AutoPupulateAttribute : Attribute
{
public string[] PropertyNames { get; set; }
public AutoPupulateAttribute(params string[] names)
{
if (names != null)
{
PropertyNames = names;
}
}
}
ValidationException.cs
public class ValidationException : Exception
{
public enum Types
{
RangeException,
OddException
}
public ValidationException(Types ExceptionType, string Message) : base(Message) { }
public ValidationException(Types ExceptionType, string Message, Exception InnerException) : base(Message, InnerException) { }
}
باز هم این صفت ها کاری انجام نمی دهند پس در اینجا لازم می شود که از امکاناتی که Reflection به ما می دهد استفاده کنیم .زمانی که شما برنامه را اجرا کنید با کمک Reflection می توانید به اشیا و همینطور صفت ها دسترسی داشته باشید و آنها را تغییر دهید .
در کد زیر متدهای الحاقی برای دستکاری صفت ها نوشته شده است
using CustomAttributes;
using FormatingAttributes;
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace Extentions
{
public static class ClassExtnetions
{
public static T AutoPopulate<t>(this T input) where T : class
{
var propertyInfos = input.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (var propertyInfo in propertyInfos)
{
var customAttributes = propertyInfo.GetCustomAttributes(true);
foreach (var customAttribute in customAttributes)
{
if (customAttribute is AutoPupulateAttribute)
{
var propNamesInfo = customAttribute.GetType().GetProperty("PropertyNames");
var propNames = (string[])propNamesInfo.GetValue(customAttribute);
var result = new StringBuilder();
foreach (var propName in propNames)
{
var propinfo = input.GetType().GetProperty(propName);
var propValue = propinfo.GetValue(input);
result.Append(propValue.ToString());
result.Append(" ");
}
propertyInfo.SetValue(input, result.ToString());
}
}
}
return input;
}
public static string ConvertToString<t>(this T input) where T : class
{
var output = new StringBuilder();
var className = input.GetType().ToString();
var properties = input.GetType().GetProperties();
output.Append($"Class Name : {className} {Environment.NewLine}");
foreach (var property in properties)
{
output.Append($"{property.Name} : {property.GetValue(input)} {Environment.NewLine}");
}
return output.ToString();
}
public static T Format<t>(this T input) where T : class
{
var propertyInfos = input.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (var propertyInfo in propertyInfos)
{
var customAttributes = propertyInfo.GetCustomAttributes(true);
foreach (var customAttribute in customAttributes)
{
if (customAttribute is ToUpperAttribute)
{
var value = propertyInfo.GetValue(input).ToString();
var customAttributeType = customAttribute.GetType().GetProperty("Type");
var type = (ToUpperTypes)customAttributeType.GetValue(customAttribute);
ToUpperAttribute(ref value, type);
propertyInfo.SetValue(input, value);
}
}
}
return input;
}
private static void ToUpperAttribute(ref string value, ToUpperTypes type)
{
switch (type)
{
case ToUpperTypes.FirstLetter:
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
return;
}
value = string.Concat(char.ToUpper(value.ToCharArray()[0]).ToString(),
value.Substring(1));
break;
case ToUpperTypes.FirstAndAfterSpace:
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
return;
}
var result = new StringBuilder();
var splittedValues = value.Split(' ');
foreach (var splittedValue in splittedValues)
{
result.Append(string.Concat(char.ToUpper(splittedValue.ToCharArray()[0]).ToString(),
splittedValue.Substring(1)));
result.Append(' ');
}
value = result.ToString();
break;
case ToUpperTypes.AllLetters:
value = value.ToUpper();
break;
}
}
public static bool Validate<t> (this T input)
{
var propertyInfos = input.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (var propertyInfo in propertyInfos)
{
return Validate(input, propertyInfo.Name);
}
return false;
}
public static bool Validate<t>(this T input, string PropertyName)
{
var propertyInfo = input.GetType().GetProperty(PropertyName);
var customAttributes = propertyInfo.GetCustomAttributes(true);
var isValid = true;
foreach (var customAttribute in customAttributes)
{
if (customAttribute is RangeValidatorAttribute)
{
var value = (int)propertyInfo.GetValue(input);
var minValueProperty = customAttribute.GetType().GetProperty("MinValue");
var maxValueProperty = customAttribute.GetType().GetProperty("MaxValue");
var minValue = (int) minValueProperty.GetValue(customAttribute);
var maxValue = (int) maxValueProperty.GetValue(customAttribute);
isValid &= RangeValidator(value, minValue, maxValue, PropertyName);
}
else if (customAttribute is IsOddNumberAttribute)
{
var value = (int)propertyInfo.GetValue(input);
if (value % 2 == 0)
{
throw new ValidationException(ValidationException.Types.OddException ,$"The value of Property {PropertyName} is {value} which is not Odd!!!");
}
isValid &=true;
}
}
return isValid;
}
private static bool RangeValidator(int value, int min, int max,string PropertyName)
{
var isValid = value <= max && value >= min;
if (!isValid)
{
throw new ValidationException(ValidationException.Types.RangeException, $"The value of property {PropertyName} is not between {min} and {max}");
}
return isValid;
}
}
}
}
همان طور که دیدید در این کلاس اعتبارسنجی ، توابع انتشار خود کار ، در داخل کلاس الحاقی ما وجود دارد .در داخل برنامه به راحتی می توانید نمونه ای از کلاس person را ایجاد کنید و تمامی توابع الحاقی گفته شده را فراخوانی کنید .
در تکه کد زیر نحوه استفاده از این توابع آورده شده است
internal class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
var persons = new List<person>();
persons.Add(
new Person()
{
Name = "john",
FamilyName = "smith dC",
Age = 22
}
);
persons.Add(
new Person()
{
Name = "Judy",
FamilyName = "Abbout Story",
Age = 65
}
);
foreach (var person in persons)
{
try
{
var isValid = person.Format().AutoPopulate().Validate();
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString());
Console.WriteLine();
if (ex is ValidationException)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
</person>
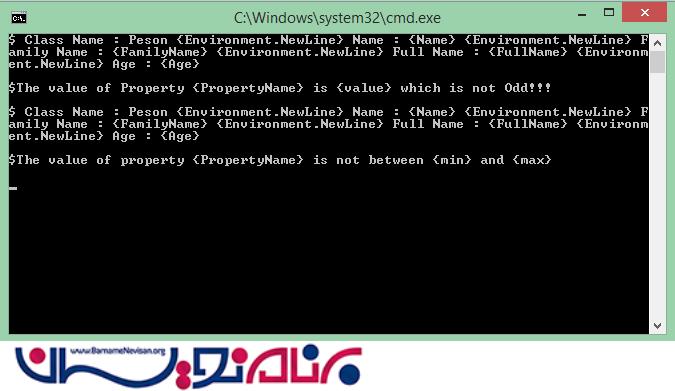
در حالت اجرا می بینید که برنامه از ما ایراد گرفته است زیرا سن یکی از اشخاصی که وارد کرده ایم خارج از محدوده 1 تا 100 است .
- C#.net
- 2k بازدید
- 1 تشکر
